Scroll down
Scroll down
Scroll down
How to Refine Carbon Black?

Key Stage in Processing Solid Residue from Used Tire Pyrolysis
This process includes a series of operations aimed at removing impurities, improving physicochemical properties, and adapting the material for reuse in industries such as rubber and plastics.
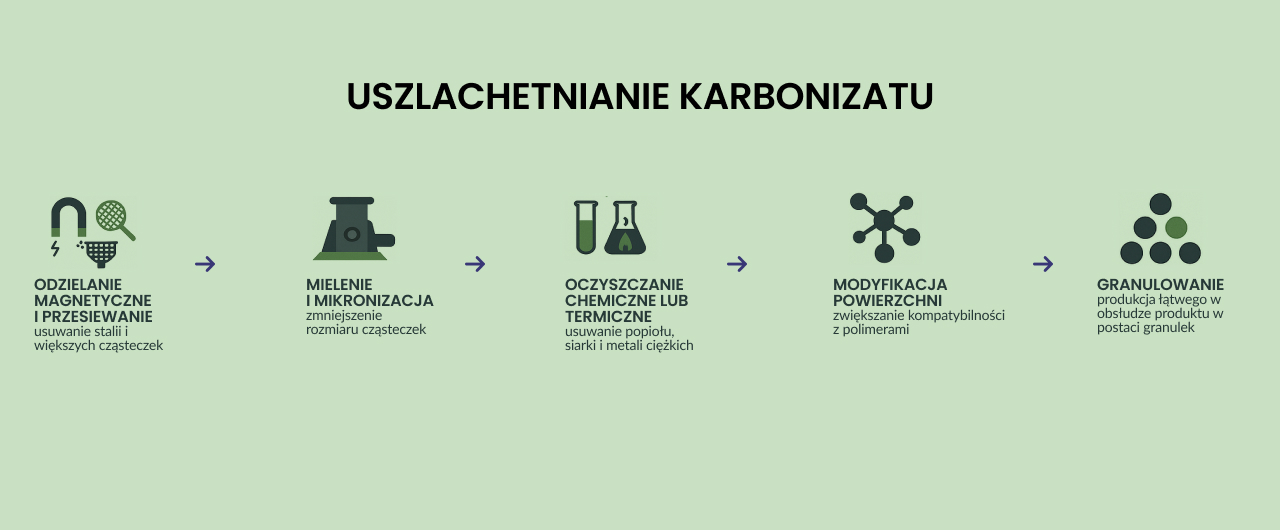
Main Stages of Carbon Black Refinement
1. Magnetic Separation and Sieving
Purpose:
Removal of ferromagnetic contaminants (e.g., steel wires from tires) and coarse solid fractions.
Technology:
Magnetic separators, vibrating screens, air classifiers.
2. Grinding and Micronization
Purpose:
Particle size reduction to required parameters; achieving uniform granulation (often below 10–30 microns).
Technology:
Ball mills, jet mills, hammer mills.
Effect:
Improved dispersibility and specific surface area, resulting in better functional properties.
3. Chemical or Thermal Purification
Purpose:
Removal of residual ash, sulfur, heavy metals, and other inorganic compounds.
Methods:
Acid leaching (most commonly with mineral acids like HCl, H₂SO₄),
Alkaline cleaning (e.g., NaOH),
Heat treatment (e.g., calcination),
Plasma or ozone treatment (less common).
Effect:
Reducing ash content from 15–20% to below 5%; increasing BET surface area.
4. Surface Modification
Purpose:
Improving compatibility of rCB with polymer matrices (e.g., in elastomers).
Methods:
Oxidation (e.g., nitric acid, ozone),
Silane or organic compound modification,
Plasma or chemical activation.
Effect:
Enhanced mechanical and rheological properties of final products.
5. Granulation or Pelletizing
Purpose:
Facilitating transport, storage, and dosing in further processes.
Effect:
Final product in granular form with high flowability and low dustiness.

